 In mathematics, a function is a rule which relates a given set of inputs to a set of possible outputs. The important point to note about a function is that each input is related to exactly one output.
In mathematics, a function is a rule which relates a given set of inputs to a set of possible outputs. The important point to note about a function is that each input is related to exactly one output.
The process of naming functions is known as function notation. The most commonly used function notation symbols include: “f(x) = …”, “g(x) = …”, “h(x) = …,” etc.
In this article, we will learn what composite functions are and how to solve them.
What is a Composite Function?
If we are given two functions, we can create another function by composing one function into the other. The steps required to perform this operation are similar to when any function is solved for any given value. Such functions are called composite functions.
A composite function is generally a function that is written inside another function. Composition of a function is done by substituting one function into another function.
For example, f [g (x)] is the composite function of f (x) and g (x). The composite function f [g (x)] is read as “f of g ofx”. The function g (x) is called an inner function and the function f (x) is called an outer function. Hence, we can also read f [g (x)] as “the function g is the inner function of the outer function f”.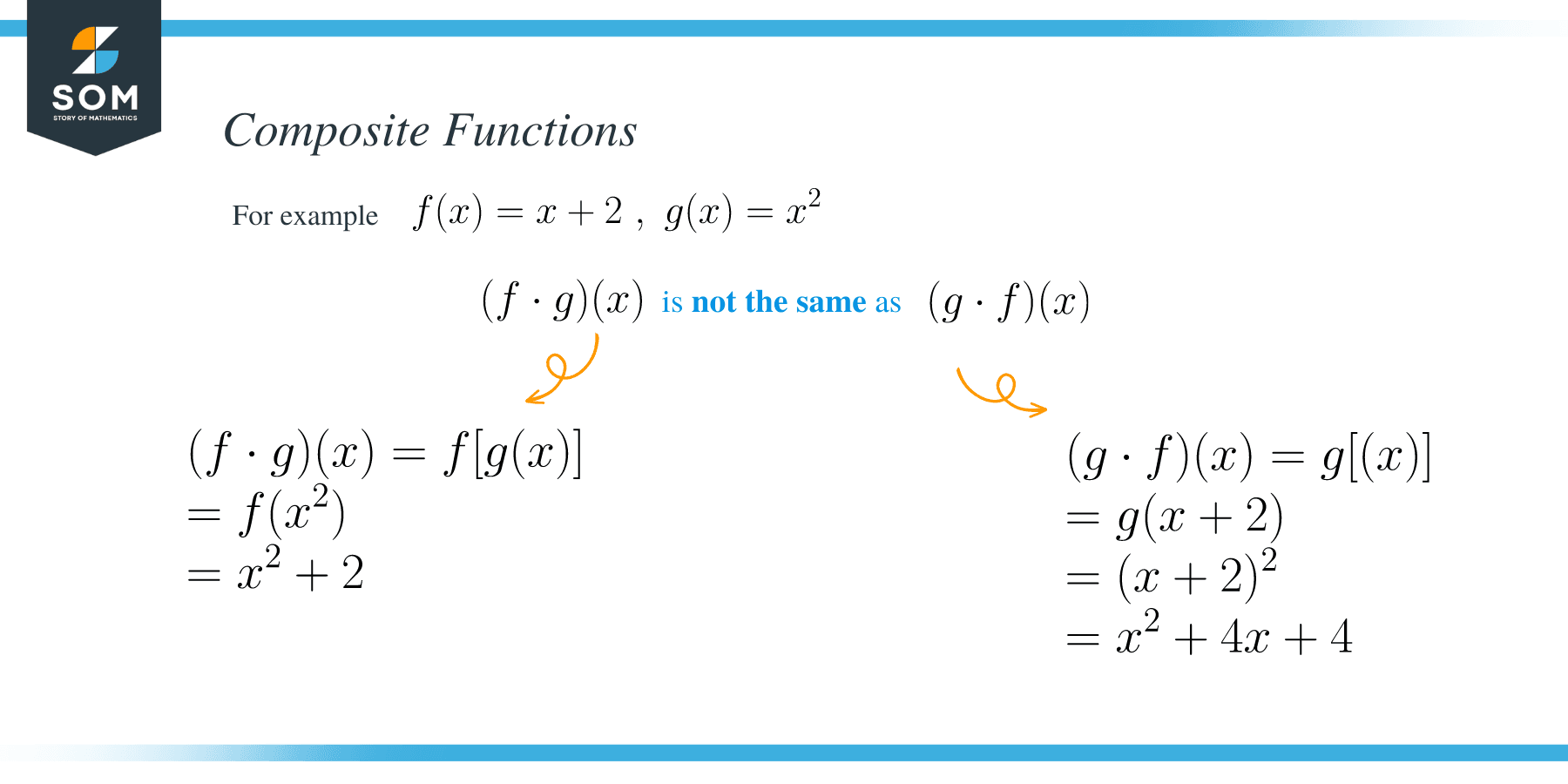
How to Solve Composite Functions?
Solving a composite function means, finding the composition of two functions. We use a small circle (∘) for the composition of a function. Here are the steps on how to solve a composite function:
- Rewritethecomposition in adifferent form.
For example
(f ∘ g) (x) = f [g (x)]
(f ∘ g) (x) =f [g (x)]
(f ∘ g) (x²)= f [g (x²)]
- Substitute the variable x that is in the outsidefunction with theinsidefunction.
- Simplify the function.
Note: The order in the composition of a function is important because (f ∘ g) (x) is NOT the same as (g ∘ f) (x).
Let’s look at the following problems:
Example 1
Given the functions f (x) =x2+ 6 and g (x) = 2x– 1, find (f ∘ g) (x).
Solution
Substitute x with 2x– 1 in the function f(x) =x2+ 6.
(f ∘ g) (x) = (2x– 1)2+ 6 = (2x – 1) (2x – 1) + 6
Apply FOIL
= 4x2– 4x+ 1 + 6
= 4x2– 4x+ 7
Example 2
Given the functions g (x) = 2x– 1 and f (x) =x2+ 6, find (g ∘ f) (x).
Solution
Substitute x with x2+ 6 in the function g (x) = 2x– 1
(g ∘ f) (x) = 2(x2+ 6) – 1
Use the distributive property to remove the parentheses.
= 2x2+ 12 – 1
= 2x2+ 11
Example 3
Given f (x) = 2x + 3, find (f ∘ f) (x).
Solution
(f ∘ f) (x) =f[f(x)]
=2(2x + 3) + 3
= 4x + 9
Example 4
Find(g∘f) (x) given that,f (x) = 2x+ 3andg (x) = –x2+ 5
⟹ (g∘ f) (x) =g [f (x)]
Replace x in g(x) = –x2+ 5 with 2x+ 3
= – (2x+ 3)2+ 5
= – (4x2+ 12x+ 9) + 5
= –4x2– 12x– 9 + 5
=–4x2– 12x– 4
Example 5
Evaluatef [g (6)] given that, f (x) = 5x + 4and g (x) = x – 3
Solution
First, find the value of f(g(x)).
⟹ f (g (x)) = 5(x – 3) + 4
= 5x – 15 + 4
= 5x – 11
Now substitute x in f(g(x)) with 6
⟹5(6) – 11
⟹ 30 – 11
= 19
Therefore, f [g (6)] = 19
Example 6
Find f [g (5)] given that, f (x) = 4x + 3 and g (x) = x – 2.
Solution
Begin by finding the value of f [g (x)].
⟹ f(x) = 4x + 3
⟹ g(x) = x – 2
f[g(x)] = 4(x – 2) + 3
= 4x – 8 + 3
= 4x – 5
Now, evaluate f [g (5)] by substituting x in f[g(x)] with 5.
f [g (x)] = 4(5) – 5
= 15
Hence, f [g (5)] = 15.
Example 7
Given g (x) = 2x + 8 and f (x) = 8x², Find (f ∘ g) (x)
Solution
(f ∘g) (x)= f [g(x)]
Replace x in f(x) = 8x² with (2x + 8)
⟹ (f ∘g) (x)= f [g(x)]=8(2x + 8) ²
⟹ 8 [4x² + 8² + 2(2x) (8)]
⟹8 [4x² + 64 + 32x]
⟹ 32x² + 512 + 256 x
⟹ 32x² + 256 x + 512
Example 8
Find (g ∘ f) (x) if, f(x) = 6 x²and g(x) = 14x + 4
Solution
⟹ (g ∘ f) (x) = g [f(x)]
Substitute x in g(x) = 14x + 4 with 6 x²
⟹g [f(x)] =14 (6 x²) + 4
= 84x² + 4
Example 9
Calculate (f ∘ g) (x) using f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = -x2+ 1,
Solution
(f ∘ g) (x) = f(g(x))
= 2 (g(x)) + 3
= 2(-x2+ 1) + 3
= – 2 x2+ 5
Example 10
Given f(x) = √ (x + 2) and g(x) = ln (1 – x2), find domain of (g∘ f) (x).
Solution
⟹ (g∘ f) (x) = g(f(x))
⟹ ln (1 – f(x)2) = ln (1 – √ (x + 2)2)
⟹ ln (1 – (x + 2))
= ln (- x – 1)
Set x + 2 to ≥ 0
Therefore, domain: [-2, -1]
Example 11
Given two functions: f = {(-2, 1), (0, 3), (4, 5)}and g = {(1, 1), (3, 3), (7, 9)}, find (g∘ f) and determine its domain and range.
Solution
⟹ (g∘f) (-2) = g [f (-2)] = g (1) = 1
⟹ (g∘f) (0) = g [f (0)] = g(3) = 3
⟹ (g∘f)(4) = g[f(4)] = g(5) = undefined
Hence, g∘f = {(-2, 1), (0, 3)}
Therefore, Domain: {-2, 0} and Range: {1, 3}
